3DPRINTINGINDUSTRY.COM
UC Berkeley Unveils $5,000, Customizable Humanoid Robot for Open-Source Collaboration
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have introduced the Berkeley Humanoid Lite, a customizable, 3D printable humanoid robot designed for researchers, educators, and hobbyists. Unlike commercial humanoid robots, which can cost upwards of $100,000, the Berkeley Humanoid Lite can be assembled for under $5,000 using standard parts and desktop 3D printers.
“Despite significant advancements in humanoid robotics, many commercially available systems are expensive, closed-source, and inaccessible to the wider robotics community,” the research team stated. “This lack of transparency and customization limits progress in the field. The Berkeley Humanoid Lite addresses these challenges by providing an open-source, customizable solution that is more accessible and adaptable for researchers and practitioners.”
Berkeley Humanoid Lite teleoperation setup. Photo via University of California, Berkeley.
3D Printed Components and Open-Source Development
The Berkeley Humanoid Lite project was developed by a multidisciplinary team of UC Berkeley researchers, including PhD students Yufeng Chi, Qiyayuan Liao, Junfeng Long, Xiaoyu Huang, and Zhongyu Li, alongside Associate Professors Sophia Shao, Borivoje Nikolic, and Koushil Sreenath.
The design of the Berkeley Humanoid Lite emphasizes modularity and ease of fabrication, featuring a 3D printed modular gearbox for the actuators and robot body. All components can be sourced from widely available e-commerce platforms and produced using standard desktop 3D printers.
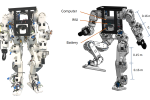
Standing at 0.8 meters tall and weighing 16 kilograms, the robot incorporates aluminum components to provide added structural support. A key feature of the Berkeley Humanoid Lite is its use of 3D printed cycloidal gearboxes, which help optimize efficiency and reduce production costs, while addressing common limitations of 3D printed gear systems, such as lower strength and durability compared to metal alternatives.
Berkeley Humanoid Lite. Image via: University of California, Berkeley.
The team demonstrated the real-world applicability of the platform through a series of locomotion and teleoperation experiments. By integrating a reinforcement learning-based locomotion controller, they achieve successful zero-shot policy transfer from simulation to hardware, validating the effectiveness of the actuator design in dynamic tasks. The robot is capable of performing a wide range of tasks, including walking, writing, unpacking, packing, solving a Rubik’s Cube, and responding to remote control commands.
Snapshot of teleoperated manipulation experiments, including four tasks: writing, unpacking and packing, picking and placing blocks, and solving Rubik’s Cube. Photo via University of California, Berkeley.
In support of open collaboration and the democratization of humanoid robots, the researchers have made the full design—including CAD files, programming code, and training resources—freely available at https://lite.berkeley-humanoid.org. By releasing all materials as open-source, they aim to expand access and encourage collaboration within the robotics community.
Humanoid Robots and 3D Printing Advancements
In 2018, Boston Dynamics released a video showcasing the Atlas humanoid robot’s capabilities, which included jogging, navigating inclines and uneven terrain, and jumping over a log for search-and-rescue purposes. Initially unveiled in 2013 as a DARPA prototype, Atlas started with basic walking capabilities, similar to a toddler’s movements, and has since evolved to demonstrate highly complex and dynamic movement patterns.
In the same year, Intel, in partnership with USC, Olin College, and Trossen Robotics, introduced Jimmy, a 3D printed, open-source humanoid robot designed to feature advanced capabilities. Priced at $16,000, Jimmy was created to serve as a base model for the development of a more affordable and adaptable android, with the aim of fostering collaboration within the open-source robotics community. The robot’s design emphasized the integration of advanced functionality while providing opportunities for modification and improvement by developers.
What 3D printing trends should you watch out for in 2025?
How is the future of 3D printing shaping up?
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us onLinkedIn.
While you’re here, why not subscribe to our YouTube channel? Featuring discussion, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Featured image shows Berkeley Humanoid Lite. Image via: University of California, Berkeley.
Paloma Duran
Paloma Duran holds a BA in International Relations and an MA in Journalism. Specializing in writing, podcasting, and content and event creation, she works across politics, energy, mining, and technology. With a passion for global trends, Paloma is particularly interested in the impact of technology like 3D printing on shaping our future.