The U.S. Ran Its First Space Weather Preparedness Drill—Here's How It Went
The U.S. Ran Its First Space Weather Preparedness Drill—Here’s How It Went
Ironically, the exercise last May was interrupted by a real scenario, when Earth was hit by the strongest solar storm in two decades
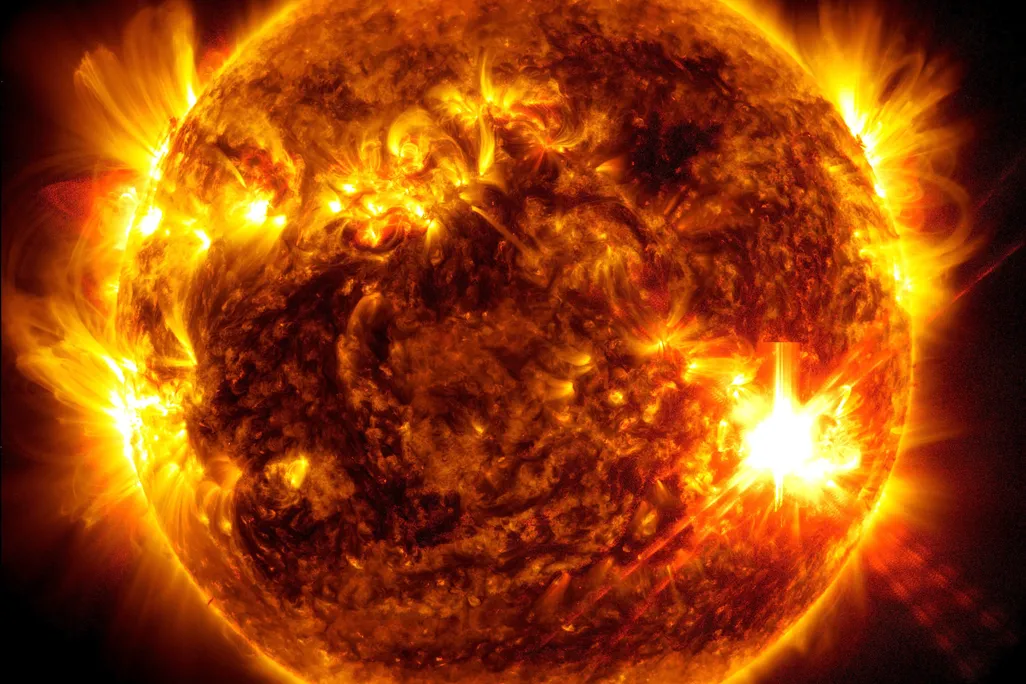
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatorycaptured this image of extreme solar activity on May 10, 2024.
NASA SDO
In May last year, the United States government hosted its first-ever “Space Weather Tabletop Exercise,” a hypothetical practice test to determine whether the country is prepared for space weather events, such as intense geomagnetic storms.
The exercise brought together agencies such as NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administrationand the Department of Homeland Security to talk through how they would handle such a threat—and the risks it would pose to Earth.
“Minimizing the impacts of such storms requires close coordination, and this meeting was their chance to practice,” reads a NASA statement.
The outcome of the test? State and federal agencies found out they need all the practice they can get.
“Overall, the exercise demonstrated the need for better coordination to produce meaningfulnotifications that describe the potential impacts to critical infrastructure,” reads the post-exercise report, “as well as emphasized the importance of the whole-of-government planning approach for significantevents.”
Geomagnetic storms are strong disturbances in Earth’s magnetic field, and they can result from solar storms: explosions of material including energy, particles and magnetic fields from the sun’s surface, which can include solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Geomagnetic storms can wreck satellites, trigger radio blackouts and power outages and endanger astronauts by exposing them to intense radiation, according to the statement.
Extreme geomagnetic storms only occur every few decades, per Live Science’s Tereza Pultarova. But our society has become so dependent on vulnerable technologies that the impact of space weather today could be significant.
On May 8 and 9, 2024, participants at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Maryland and the Federal Emergency Management Agency office in Colorado pretended it was January 2028, and they had to work through hypothetical scenarios involving harmful solar activity. At the beginning of the exercise, NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center notified participants that an active region on the sun had rotated to a point that, if it exploded, it could impact Earth. To make matters worse, two NASA astronauts were in a spacecraft orbiting the moon, with two of their colleagues currently on the lunar surface.
The scenario quickly introduced harmful solar activity. Hypothetical effects included satellites, astronauts and airplanes exposed to intense radiation; disrupted or blocked radio communication and GPS systems; degraded communication with orbiting satellites and widespread power outages.
One issue the report highlights is that space weather forecasters have very little time to determine the potential impact of the sun’s coronal mass ejections. They can’t measure the CME until it passes satellites at the first Lagrange point, a gravitationally stable location that’s about 930,000 miles from Earth.
“We never know … what the CME is composed of and what to make of it until it gets just one million miles from Earth, where it’s only 15 to 45 minutes away,” Shawn Dahl, senior space weather forecaster at the Space Weather Prediction Center, told Gizmodo’s Passant Rabie in August. “That’s when we can see what the CME is composed of. How strong is it magnetically? What’s the speed of its movement? Is it going to connect with Earth?”
According to the NASA statement, the exercise demonstrated “a critical need” for “more robust forecasting capabilities of space weather drivers and effects.” The report also emphasizes the need to educate the public, continue developing response plans, make critical infrastructure less vulnerable and collaborate with both the private sector and international agencies.
What Happened During the Biggest Geomagnetic Storm in More than 20 Years
Watch on
Notably, the hypothetical exercise last year was interrupted by a real one, when Earth was hit by the most severe solar storm in more than 20 years, now named the Gannon storm. That staggering event, which first struck our planet on May 10, 2024, provided a real-world example for scientists to study.
“These extraordinary events required key participants to simultaneously manage both simulated actions of theand the real-world needs of the nation,” according to a statement from NOAA.
The storm tripped high-voltage lines, overheated transformers, interfered with GPS-guided farm equipment and re-routed flights over the Atlantic Ocean. The atmosphere expanded from heat, reaching a whopping 2,100 degrees Fahrenheit, and that led to increased drag on satellites. It super-charged the magnetosphere with the largest electric current seen in 20 years, and it temporarily restructured the planet’s ionosphere.
Participants reported that running through the hypothetical scenario generated important conversations and improved communication across agencies. Still, it remains to be seen how prepared we’ll be next time an angry solar region turns our way.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
#ran #its #first #space #weatherThe U.S. Ran Its First Space Weather Preparedness Drill—Here's How It Went
The U.S. Ran Its First Space Weather Preparedness Drill—Here’s How It Went
Ironically, the exercise last May was interrupted by a real scenario, when Earth was hit by the strongest solar storm in two decades
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatorycaptured this image of extreme solar activity on May 10, 2024.
NASA SDO
In May last year, the United States government hosted its first-ever “Space Weather Tabletop Exercise,” a hypothetical practice test to determine whether the country is prepared for space weather events, such as intense geomagnetic storms.
The exercise brought together agencies such as NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administrationand the Department of Homeland Security to talk through how they would handle such a threat—and the risks it would pose to Earth.
“Minimizing the impacts of such storms requires close coordination, and this meeting was their chance to practice,” reads a NASA statement.
The outcome of the test? State and federal agencies found out they need all the practice they can get.
“Overall, the exercise demonstrated the need for better coordination to produce meaningfulnotifications that describe the potential impacts to critical infrastructure,” reads the post-exercise report, “as well as emphasized the importance of the whole-of-government planning approach for significantevents.”
Geomagnetic storms are strong disturbances in Earth’s magnetic field, and they can result from solar storms: explosions of material including energy, particles and magnetic fields from the sun’s surface, which can include solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Geomagnetic storms can wreck satellites, trigger radio blackouts and power outages and endanger astronauts by exposing them to intense radiation, according to the statement.
Extreme geomagnetic storms only occur every few decades, per Live Science’s Tereza Pultarova. But our society has become so dependent on vulnerable technologies that the impact of space weather today could be significant.
On May 8 and 9, 2024, participants at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Maryland and the Federal Emergency Management Agency office in Colorado pretended it was January 2028, and they had to work through hypothetical scenarios involving harmful solar activity. At the beginning of the exercise, NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center notified participants that an active region on the sun had rotated to a point that, if it exploded, it could impact Earth. To make matters worse, two NASA astronauts were in a spacecraft orbiting the moon, with two of their colleagues currently on the lunar surface.
The scenario quickly introduced harmful solar activity. Hypothetical effects included satellites, astronauts and airplanes exposed to intense radiation; disrupted or blocked radio communication and GPS systems; degraded communication with orbiting satellites and widespread power outages.
One issue the report highlights is that space weather forecasters have very little time to determine the potential impact of the sun’s coronal mass ejections. They can’t measure the CME until it passes satellites at the first Lagrange point, a gravitationally stable location that’s about 930,000 miles from Earth.
“We never know … what the CME is composed of and what to make of it until it gets just one million miles from Earth, where it’s only 15 to 45 minutes away,” Shawn Dahl, senior space weather forecaster at the Space Weather Prediction Center, told Gizmodo’s Passant Rabie in August. “That’s when we can see what the CME is composed of. How strong is it magnetically? What’s the speed of its movement? Is it going to connect with Earth?”
According to the NASA statement, the exercise demonstrated “a critical need” for “more robust forecasting capabilities of space weather drivers and effects.” The report also emphasizes the need to educate the public, continue developing response plans, make critical infrastructure less vulnerable and collaborate with both the private sector and international agencies.
What Happened During the Biggest Geomagnetic Storm in More than 20 Years
Watch on
Notably, the hypothetical exercise last year was interrupted by a real one, when Earth was hit by the most severe solar storm in more than 20 years, now named the Gannon storm. That staggering event, which first struck our planet on May 10, 2024, provided a real-world example for scientists to study.
“These extraordinary events required key participants to simultaneously manage both simulated actions of theand the real-world needs of the nation,” according to a statement from NOAA.
The storm tripped high-voltage lines, overheated transformers, interfered with GPS-guided farm equipment and re-routed flights over the Atlantic Ocean. The atmosphere expanded from heat, reaching a whopping 2,100 degrees Fahrenheit, and that led to increased drag on satellites. It super-charged the magnetosphere with the largest electric current seen in 20 years, and it temporarily restructured the planet’s ionosphere.
Participants reported that running through the hypothetical scenario generated important conversations and improved communication across agencies. Still, it remains to be seen how prepared we’ll be next time an angry solar region turns our way.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
#ran #its #first #space #weather