A Methane-Spewing Mud Volcano Gives Sanctuary to Arctic Seafloor Species
www.discovermagazine.com
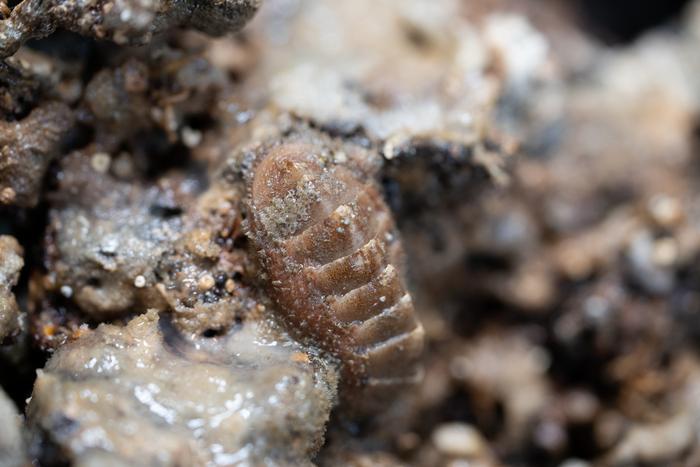
Deep in the Barents Sea off the northern coast of Norway, the Borealis Mud Volcano has been spewing methane for centuries and supporting a flourishing community of seafloor creatures. Researchers have now recognized the underwater structure as a pillar of marine life in the benthic zone, the lowest ecological region of a body of water, where species are specially equipped to survive extreme living conditions.The distinctive environment has been detailed in a new study published in Nature Communications. The international research team involved with the study put a particular focus on the importance of the mud volcanos methane emissions; normally methane is associated with greenhouse gas and climate impacts, but it also plays an important role in forming complex, biodiverse ecosystems like the one surrounding Borealis.Living On the CrustsFirst discovered in 2023, the Borealis Mud Volcano is distinguished by a cluster of craters within a depression around 1,600 feet to 2,000 feet in diameter and an active gryphon, which is a steep cone that expels mud and other fluids, gasses, and oils. Borealis is only the second mud volcano to be observed in Norwegian waters, the first being the Hkon Mosby Mud Volcano discovered during a 1987 expedition.The mud volcano is considered a cold seep environment, a location where fluids containing methane, hydrogen sulfide, or other hydrocarbons seep up from below the seafloor (cold refers to the fact that it is not as warm as the conditions around hydrothermal vents).While some sections of the crater floor are inhospitable, the researchers found several species living on the volcanos carbonate crusts. These structures are created in part by a type of chemosynthesis, the biological process by which deep-sea microorganisms use energy to produce sugars (food) since sunlight generally does not reach the benthic zone; the particular type of chemosynthesis in this case is called anaerobic oxidation of methane, which increases local alkalinity and leads to the accumulation of carbonate deposits.The extent of carbonate deposits at Borealis indicate that the mud volcano has likely been producing methane for thousands of years, the researchers say.A Seafloor RefugeExploring the carbonate crusts with a remotely operated vehicle, the researchers spotted species of anemones, serpulids, demosponges, and octocoral colonies. Also present at the jagged carbonate formations were schools of fish, including saithe (or pollock), wolffish, cod, four-bearded rockling, and several species of Sebastes (many known as redfish).Researchers consider the Borealis mud volcano an oasis that provides shelter and feeding opportunities for thriving species, almost like a reef habitat. It acts as a refuge for species that are becoming increasingly endangered, including redfish species, many of which have been placed on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red List. The Borealis Mud Volcano is a unique geological and ecological phenomenon that provides a rare insight into the complex interactions between geological processes and marine ecosystems. It is important to preserve these unique habitats, which play a crucial role in maintaining marine biodiversity, said Giuliana Panieri, a geology professor at UiT The Arctic University of Norway and lead author of the study, in a statement.The immediate surroundings of the mud volcano, researchers found, were warmed to 11.5 degrees Celsius (52.7 degrees Fahrenheit), whereas the seabed usually has a colder temperature of around 4 degrees Celsius (39.2 degrees Fahrenheit). In addition, they came across sediments that contained extinct, microscopic marine organisms from up to 2.5 million years ago.The Future of the Deep SeaThe new insight on Borealis is relevant as the Arctic seabed could soon become a center for deep-sea mining, posing a major threat to seafloor environments. Researchers say there is also a need to study the methane emissions of the mud volcano on a deeper level. Although the impact of underwater methane emissions on carbon in the atmosphere is thought to be relatively minor, we still need to know how the emissions will fully affect the planet as it warms. Seafloor conservation in Norway, meanwhile, has promised progress. The nation has pledged to reach the 30 by 30 target, which entails protecting 30 percent of land and sea by 2030. A significant portion of this involves conservation measures for marine ecosystems, including those in the deep sea. By protecting the seafloor, scientists suggest that more cold seep environments could start to see the growth of biodiversity. Article SourcesOur writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed studies and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors review for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources used below for this article:NOAA Ocean Exploration. What is the difference between cold seeps and hydrothermal vents?Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Life at Vents & SeepsJack Knudson is an assistant editor at Discover with a strong interest in environmental science and history. Before joining Discover in 2023, he studied journalism at the Scripps College of Communication at Ohio University and previously interned at Recycling Today magazine.
0 Σχόλια
·0 Μοιράστηκε
·64 Views