Research roundup: 7 stories we almost missed
Best of the rest
Research roundup: 7 stories we almost missed
Also: drumming chimpanzees, picking styles of two jazz greats, and an ancient underground city's soundscape
Jennifer Ouellette
–
May 31, 2025 5:37 pm
|
4
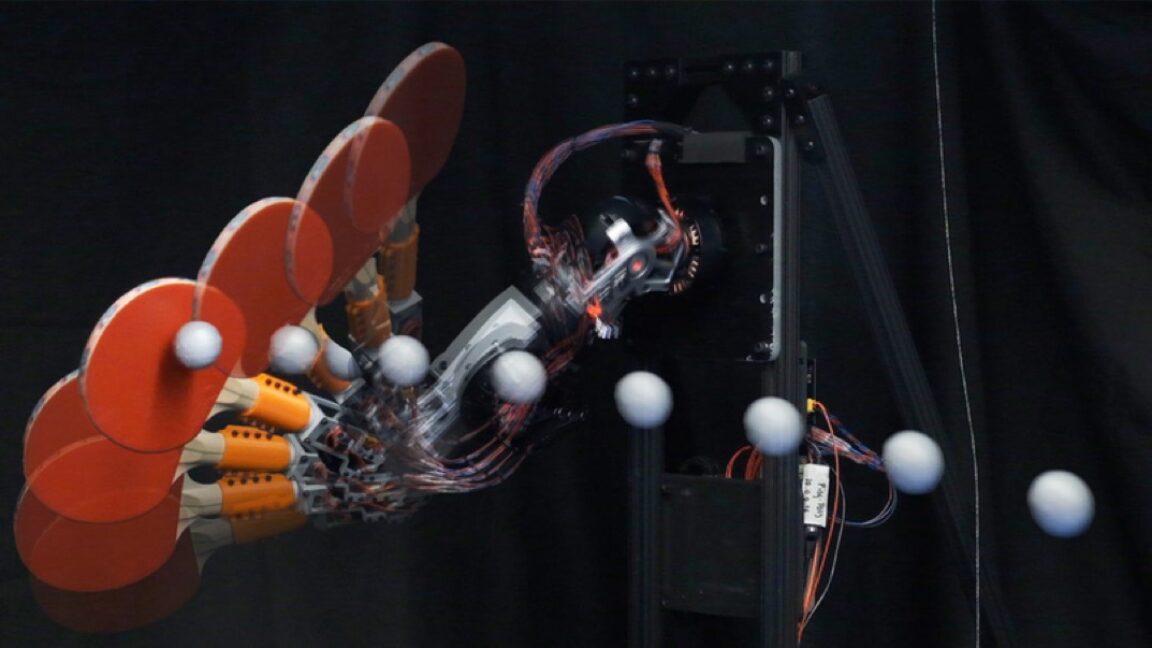
Time lapse photos show a new ping-pong-playing robot performing a top spin.
Credit:
David Nguyen, Kendrick Cancio and Sangbae Kim
Time lapse photos show a new ping-pong-playing robot performing a top spin.
Credit:
David Nguyen, Kendrick Cancio and Sangbae Kim
Story text
Size
Small
Standard
Large
Width
*
Standard
Wide
Links
Standard
Orange
* Subscribers only
Learn more
It's a regrettable reality that there is never time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. In the past, we've featured year-end roundups of cool science stories wemissed. This year, we're experimenting with a monthly collection. May's list includes a nifty experiment to make a predicted effect of special relativity visible; a ping-pong playing robot that can return hits with 88 percent accuracy; and the discovery of the rare genetic mutation that makes orange cats orange, among other highlights.
Special relativity made visible
Credit:
TU Wien
Perhaps the most well-known feature of Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity is time dilation and length contraction. In 1959, two physicists predicted another feature of relativistic motion: an object moving near the speed of light should also appear to be rotated. It's not been possible to demonstrate this experimentally, however—until now. Physicists at the Vienna University of Technology figured out how to reproduce this rotational effect in the lab using laser pulses and precision cameras, according to a paper published in the journal Communications Physics.
They found their inspiration in art, specifically an earlier collaboration with an artist named Enar de Dios Rodriguez, who collaborated with VUT and the University of Vienna on a project involving ultra-fast photography and slow light. For this latest research, they used objects shaped like a cube and a sphere and moved them around the lab while zapping them with ultrashort laser pulses, recording the flashes with a high-speed camera.
Getting the timing just right effectively yields similar results to a light speed of 2 m/s. After photographing the objects many times using this method, the team then combined the still images into a single image. The results: the cube looked twisted and the sphere's North Pole was in a different location—a demonstration of the rotational effect predicted back in 1959.
DOI: Communications Physics, 2025. 10.1038/s42005-025-02003-6 .
Drumming chimpanzees
A chimpanzee feeling the rhythm. Credit: Current Biology/Eleuteri et al., 2025.
Chimpanzees are known to "drum" on the roots of trees as a means of communication, often combining that action with what are known as "pant-hoot" vocalizations. Scientists have found that the chimps' drumming exhibits key elements of musical rhythm much like humans, according to a paper published in the journal Current Biology—specifically non-random timing and isochrony. And chimps from different geographical regions have different drumming rhythms.
Back in 2022, the same team observed that individual chimps had unique styles of "buttress drumming," which served as a kind of communication, letting others in the same group know their identity, location, and activity. This time around they wanted to know if this was also true of chimps living in different groups and whether their drumming was rhythmic in nature. So they collected video footage of the drumming behavior among 11 chimpanzee communities across six populations in East Africaand West Africa, amounting to 371 drumming bouts.
Their analysis of the drum patterns confirmed their hypothesis. The western chimps drummed in regularly spaced hits, used faster tempos, and started drumming earlier during their pant-hoot vocalizations. Eastern chimps would alternate between shorter and longer spaced hits. Since this kind of rhythmic percussion is one of the earliest evolved forms of human musical expression and is ubiquitous across cultures, findings such as this could shed light on how our love of rhythm evolved.
DOI: Current Biology, 2025. 10.1016/j.cub.2025.04.019 .
Distinctive styles of two jazz greats
Jazz lovers likely need no introduction to Joe Pass and Wes Montgomery, 20th century guitarists who influenced generations of jazz musicians with their innovative techniques. Montgomery, for instance, didn't use a pick, preferring to pluck the strings with his thumb—a method he developed because he practiced at night after working all day as a machinist and didn't want to wake his children or neighbors. Pass developed his own range of picking techniques, including fingerpicking, hybrid picking, and "flat picking."
Chirag Gokani and Preston Wilson, both with Applied Research Laboratories and the University of Texas, Austin, greatly admired both Pass and Montgomery and decided to explore the underlying the acoustics of their distinctive playing, modeling the interactions of the thumb, fingers, and pick with a guitar string. They described their research during a meeting of the Acoustical Society of America in New Orleans, LA.
Among their findings: Montgomery achieved his warm tone by playing closer to the bridge and mostly plucking at the string. Pass's rich tone arose from a combination of using a pick and playing closer to the guitar neck. There were also differences in how much a thumb, finger, and pick slip off the string: use of the thumbproduced more of a "pluck" compared to the pick, which produced more of a "strike." Gokani and Wilson think their model could be used to synthesize digital guitars with a more realistic sound, as well as helping guitarists better emulate Pass and Montgomery.
Sounds of an ancient underground city
Credit:
Sezin Nas
Turkey is home to the underground city Derinkuyu, originally carved out inside soft volcanic rock around the 8th century BCE. It was later expanded to include four main ventilation channelsserving seven levels, which could be closed off from the inside with a large rolling stone. The city could hold up to 20,000 people and it was connected to another underground city, Kaymakli, via tunnels. Derinkuyu helped protect Arab Muslims during the Arab-Byzantine wars, served as a refuge from the Ottomans in the 14th century, and as a haven for Armenians escaping persecution in the early 20th century, among other functions.
The tunnels were rediscovered in the 1960s and about half of the city has been open to visitors since 2016. The site is naturally of great archaeological interest, but there has been little to no research on the acoustics of the site, particularly the ventilation channels—one of Derinkuyu's most unique features, according to Sezin Nas, an architectural acoustician at Istanbul Galata University in Turkey. She gave a talk at a meeting of the Acoustical Society of America in New Orleans, LA, about her work on the site's acoustic environment.
Nas analyzed a church, a living area, and a kitchen, measuring sound sources and reverberation patterns, among other factors, to create a 3D virtual soundscape. The hope is that a better understanding of this aspect of Derinkuyu could improve the design of future underground urban spaces—as well as one day using her virtual soundscape to enable visitors to experience the sounds of the city themselves.
MIT's latest ping-pong robot
Robots playing ping-pong have been a thing since the 1980s, of particular interest to scientists because it requires the robot to combine the slow, precise ability to grasp and pick up objects with dynamic, adaptable locomotion. Such robots need high-speed machine vision, fast motors and actuators, precise control, and the ability to make accurate predictions in real time, not to mention being able to develop a game strategy. More recent designs use AI techniques to allow the robots to "learn" from prior data to improve their performance.
MIT researchers have built their own version of a ping-pong playing robot, incorporating a lightweight design and the ability to precisely return shots. They built on prior work developing the Humanoid, a small bipedal two-armed robot—specifically, modifying the Humanoid's arm by adding an extra degree of freedom to the wrist so the robot could control a ping-pong paddle. They tested their robot by mounting it on a ping-pong table and lobbing 150 balls at it from the other side of the table, capturing the action with high-speed cameras.
The new bot can execute three different swing typesand during the trial runs it returned the ball with impressive accuracy across all three types: 88.4 percent, 89.2 percent, and 87.5 percent, respectively. Subsequent tweaks to theirrystem brought the robot's strike speed up to 19 meters per second, close to the 12 to 25 meters per second of advanced human players. The addition of control algorithms gave the robot the ability to aim. The robot still has limited mobility and reach because it has to be fixed to the ping-pong table but the MIT researchers plan to rig it to a gantry or wheeled platform in the future to address that shortcoming.
Why orange cats are orange
Credit:
Astropulse/CC BY-SA 3.0
Cat lovers know orange cats are special for more than their unique coloring, but that's the quality that has intrigued scientists for almost a century. Sure, lots of animals have orange, ginger, or yellow hues, like tigers, orangutans, and golden retrievers. But in domestic cats that color is specifically linked to sex. Almost all orange cats are male. Scientists have now identified the genetic mutation responsible and it appears to be unique to cats, according to a paper published in the journal Current Biology.
Prior work had narrowed down the region on the X chromosome most likely to contain the relevant mutation. The scientists knew that females usually have just one copy of the mutation and in that case have tortoiseshellcoloring, although in rare cases, a female cat will be orange if both X chromosomes have the mutation. Over the last five to ten years, there has been an explosion in genome resourcesfor cats which greatly aided the team's research, along with taking additional DNA samples from cats at spay and neuter clinics.
From an initial pool of 51 candidate variants, the scientists narrowed it down to three genes, only one of which was likely to play any role in gene regulation: Arhgap36. It wasn't known to play any role in pigment cells in humans, mice, or non-orange cats. But orange cats are special; their mutationturns on Arhgap36 expression in pigment cells, thereby interfering with the molecular pathway that controls coat color in other orange-shaded mammals. The scientists suggest that this is an example of how genes can acquire new functions, thereby enabling species to better adapt and evolve.
DOI: Current Biology, 2025. 10.1016/j.cub.2025.03.075 .
Not a Roman "massacre" after all
Credit:
Martin Smith
In 1936, archaeologists excavating the Iron Age hill fort Maiden Castle in the UK unearthed dozens of human skeletons, all showing signs of lethal injuries to the head and upper body—likely inflicted with weaponry. At the time, this was interpreted as evidence of a pitched battle between the Britons of the local Durotriges tribe and invading Romans. The Romans slaughtered the native inhabitants, thereby bringing a sudden violent end to the Iron Age. At least that's the popular narrative that has prevailed ever since in countless popular articles, books, and documentaries.
But a paper published in the Oxford Journal of Archaeology calls that narrative into question. Archaeologists at Bournemouth University have re-analyzed those burials, incorporating radiocarbon dating into their efforts. They concluded that those individuals didn't die in a single brutal battle. Rather, it was Britons killing other Britons over multiple generations between the first century BCE and the first century CE—most likely in periodic localized outbursts of violence in the lead-up to the Roman conquest of Britain. It's possible there are still many human remains waiting to be discovered at the site, which could shed further light on what happened at Maiden Castle.
DOI: Oxford Journal of Archaeology, 2025. 10.1111/ojoa.12324 .
Jennifer Ouellette
Senior Writer
Jennifer Ouellette
Senior Writer
Jennifer is a senior writer at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
4 Comments
#research #roundup #stories #almost #missedResearch roundup: 7 stories we almost missed
Best of the rest
Research roundup: 7 stories we almost missed
Also: drumming chimpanzees, picking styles of two jazz greats, and an ancient underground city's soundscape
Jennifer Ouellette
–
May 31, 2025 5:37 pm
|
4
Time lapse photos show a new ping-pong-playing robot performing a top spin.
Credit:
David Nguyen, Kendrick Cancio and Sangbae Kim
Time lapse photos show a new ping-pong-playing robot performing a top spin.
Credit:
David Nguyen, Kendrick Cancio and Sangbae Kim
Story text
Size
Small
Standard
Large
Width
*
Standard
Wide
Links
Standard
Orange
* Subscribers only
Learn more
It's a regrettable reality that there is never time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. In the past, we've featured year-end roundups of cool science stories wemissed. This year, we're experimenting with a monthly collection. May's list includes a nifty experiment to make a predicted effect of special relativity visible; a ping-pong playing robot that can return hits with 88 percent accuracy; and the discovery of the rare genetic mutation that makes orange cats orange, among other highlights.
Special relativity made visible
Credit:
TU Wien
Perhaps the most well-known feature of Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity is time dilation and length contraction. In 1959, two physicists predicted another feature of relativistic motion: an object moving near the speed of light should also appear to be rotated. It's not been possible to demonstrate this experimentally, however—until now. Physicists at the Vienna University of Technology figured out how to reproduce this rotational effect in the lab using laser pulses and precision cameras, according to a paper published in the journal Communications Physics.
They found their inspiration in art, specifically an earlier collaboration with an artist named Enar de Dios Rodriguez, who collaborated with VUT and the University of Vienna on a project involving ultra-fast photography and slow light. For this latest research, they used objects shaped like a cube and a sphere and moved them around the lab while zapping them with ultrashort laser pulses, recording the flashes with a high-speed camera.
Getting the timing just right effectively yields similar results to a light speed of 2 m/s. After photographing the objects many times using this method, the team then combined the still images into a single image. The results: the cube looked twisted and the sphere's North Pole was in a different location—a demonstration of the rotational effect predicted back in 1959.
DOI: Communications Physics, 2025. 10.1038/s42005-025-02003-6 .
Drumming chimpanzees
A chimpanzee feeling the rhythm. Credit: Current Biology/Eleuteri et al., 2025.
Chimpanzees are known to "drum" on the roots of trees as a means of communication, often combining that action with what are known as "pant-hoot" vocalizations. Scientists have found that the chimps' drumming exhibits key elements of musical rhythm much like humans, according to a paper published in the journal Current Biology—specifically non-random timing and isochrony. And chimps from different geographical regions have different drumming rhythms.
Back in 2022, the same team observed that individual chimps had unique styles of "buttress drumming," which served as a kind of communication, letting others in the same group know their identity, location, and activity. This time around they wanted to know if this was also true of chimps living in different groups and whether their drumming was rhythmic in nature. So they collected video footage of the drumming behavior among 11 chimpanzee communities across six populations in East Africaand West Africa, amounting to 371 drumming bouts.
Their analysis of the drum patterns confirmed their hypothesis. The western chimps drummed in regularly spaced hits, used faster tempos, and started drumming earlier during their pant-hoot vocalizations. Eastern chimps would alternate between shorter and longer spaced hits. Since this kind of rhythmic percussion is one of the earliest evolved forms of human musical expression and is ubiquitous across cultures, findings such as this could shed light on how our love of rhythm evolved.
DOI: Current Biology, 2025. 10.1016/j.cub.2025.04.019 .
Distinctive styles of two jazz greats
Jazz lovers likely need no introduction to Joe Pass and Wes Montgomery, 20th century guitarists who influenced generations of jazz musicians with their innovative techniques. Montgomery, for instance, didn't use a pick, preferring to pluck the strings with his thumb—a method he developed because he practiced at night after working all day as a machinist and didn't want to wake his children or neighbors. Pass developed his own range of picking techniques, including fingerpicking, hybrid picking, and "flat picking."
Chirag Gokani and Preston Wilson, both with Applied Research Laboratories and the University of Texas, Austin, greatly admired both Pass and Montgomery and decided to explore the underlying the acoustics of their distinctive playing, modeling the interactions of the thumb, fingers, and pick with a guitar string. They described their research during a meeting of the Acoustical Society of America in New Orleans, LA.
Among their findings: Montgomery achieved his warm tone by playing closer to the bridge and mostly plucking at the string. Pass's rich tone arose from a combination of using a pick and playing closer to the guitar neck. There were also differences in how much a thumb, finger, and pick slip off the string: use of the thumbproduced more of a "pluck" compared to the pick, which produced more of a "strike." Gokani and Wilson think their model could be used to synthesize digital guitars with a more realistic sound, as well as helping guitarists better emulate Pass and Montgomery.
Sounds of an ancient underground city
Credit:
Sezin Nas
Turkey is home to the underground city Derinkuyu, originally carved out inside soft volcanic rock around the 8th century BCE. It was later expanded to include four main ventilation channelsserving seven levels, which could be closed off from the inside with a large rolling stone. The city could hold up to 20,000 people and it was connected to another underground city, Kaymakli, via tunnels. Derinkuyu helped protect Arab Muslims during the Arab-Byzantine wars, served as a refuge from the Ottomans in the 14th century, and as a haven for Armenians escaping persecution in the early 20th century, among other functions.
The tunnels were rediscovered in the 1960s and about half of the city has been open to visitors since 2016. The site is naturally of great archaeological interest, but there has been little to no research on the acoustics of the site, particularly the ventilation channels—one of Derinkuyu's most unique features, according to Sezin Nas, an architectural acoustician at Istanbul Galata University in Turkey. She gave a talk at a meeting of the Acoustical Society of America in New Orleans, LA, about her work on the site's acoustic environment.
Nas analyzed a church, a living area, and a kitchen, measuring sound sources and reverberation patterns, among other factors, to create a 3D virtual soundscape. The hope is that a better understanding of this aspect of Derinkuyu could improve the design of future underground urban spaces—as well as one day using her virtual soundscape to enable visitors to experience the sounds of the city themselves.
MIT's latest ping-pong robot
Robots playing ping-pong have been a thing since the 1980s, of particular interest to scientists because it requires the robot to combine the slow, precise ability to grasp and pick up objects with dynamic, adaptable locomotion. Such robots need high-speed machine vision, fast motors and actuators, precise control, and the ability to make accurate predictions in real time, not to mention being able to develop a game strategy. More recent designs use AI techniques to allow the robots to "learn" from prior data to improve their performance.
MIT researchers have built their own version of a ping-pong playing robot, incorporating a lightweight design and the ability to precisely return shots. They built on prior work developing the Humanoid, a small bipedal two-armed robot—specifically, modifying the Humanoid's arm by adding an extra degree of freedom to the wrist so the robot could control a ping-pong paddle. They tested their robot by mounting it on a ping-pong table and lobbing 150 balls at it from the other side of the table, capturing the action with high-speed cameras.
The new bot can execute three different swing typesand during the trial runs it returned the ball with impressive accuracy across all three types: 88.4 percent, 89.2 percent, and 87.5 percent, respectively. Subsequent tweaks to theirrystem brought the robot's strike speed up to 19 meters per second, close to the 12 to 25 meters per second of advanced human players. The addition of control algorithms gave the robot the ability to aim. The robot still has limited mobility and reach because it has to be fixed to the ping-pong table but the MIT researchers plan to rig it to a gantry or wheeled platform in the future to address that shortcoming.
Why orange cats are orange
Credit:
Astropulse/CC BY-SA 3.0
Cat lovers know orange cats are special for more than their unique coloring, but that's the quality that has intrigued scientists for almost a century. Sure, lots of animals have orange, ginger, or yellow hues, like tigers, orangutans, and golden retrievers. But in domestic cats that color is specifically linked to sex. Almost all orange cats are male. Scientists have now identified the genetic mutation responsible and it appears to be unique to cats, according to a paper published in the journal Current Biology.
Prior work had narrowed down the region on the X chromosome most likely to contain the relevant mutation. The scientists knew that females usually have just one copy of the mutation and in that case have tortoiseshellcoloring, although in rare cases, a female cat will be orange if both X chromosomes have the mutation. Over the last five to ten years, there has been an explosion in genome resourcesfor cats which greatly aided the team's research, along with taking additional DNA samples from cats at spay and neuter clinics.
From an initial pool of 51 candidate variants, the scientists narrowed it down to three genes, only one of which was likely to play any role in gene regulation: Arhgap36. It wasn't known to play any role in pigment cells in humans, mice, or non-orange cats. But orange cats are special; their mutationturns on Arhgap36 expression in pigment cells, thereby interfering with the molecular pathway that controls coat color in other orange-shaded mammals. The scientists suggest that this is an example of how genes can acquire new functions, thereby enabling species to better adapt and evolve.
DOI: Current Biology, 2025. 10.1016/j.cub.2025.03.075 .
Not a Roman "massacre" after all
Credit:
Martin Smith
In 1936, archaeologists excavating the Iron Age hill fort Maiden Castle in the UK unearthed dozens of human skeletons, all showing signs of lethal injuries to the head and upper body—likely inflicted with weaponry. At the time, this was interpreted as evidence of a pitched battle between the Britons of the local Durotriges tribe and invading Romans. The Romans slaughtered the native inhabitants, thereby bringing a sudden violent end to the Iron Age. At least that's the popular narrative that has prevailed ever since in countless popular articles, books, and documentaries.
But a paper published in the Oxford Journal of Archaeology calls that narrative into question. Archaeologists at Bournemouth University have re-analyzed those burials, incorporating radiocarbon dating into their efforts. They concluded that those individuals didn't die in a single brutal battle. Rather, it was Britons killing other Britons over multiple generations between the first century BCE and the first century CE—most likely in periodic localized outbursts of violence in the lead-up to the Roman conquest of Britain. It's possible there are still many human remains waiting to be discovered at the site, which could shed further light on what happened at Maiden Castle.
DOI: Oxford Journal of Archaeology, 2025. 10.1111/ojoa.12324 .
Jennifer Ouellette
Senior Writer
Jennifer Ouellette
Senior Writer
Jennifer is a senior writer at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
4 Comments
#research #roundup #stories #almost #missed