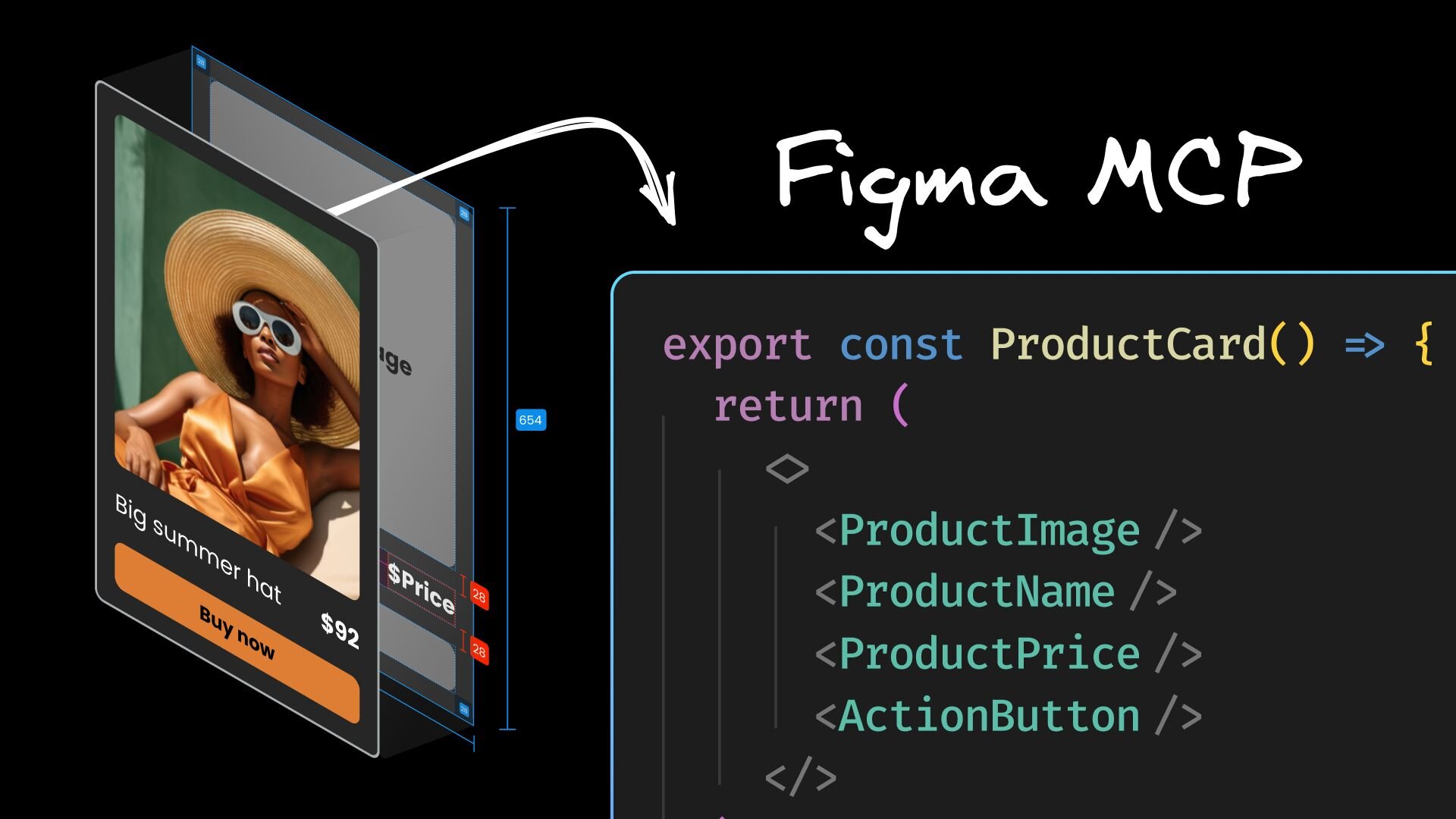
Design to Code with the Figma MCP Server
Translating your Figma designs into code can feel exactly like the kind of frustrating, low-skill gruntwork that's perfect for AI... except that most of us have also watched AI butcher hopeful screenshots into unresponsive spaghetti.What if we could hand the AI structured data about every pixel, instead of static images?This is how Figma Model Context Protocolservers work. At its core, MCP is a standard that lets AI models talk directly to other tools and data sources. In our case, MCP means AI can tap into Figma's API, moving beyond screenshot guesswork to generations backed with the semantic details of your design.Figma has its own official MCP server in private alpha, which will be the best case scenario for ongoing standardization with Figma's API, but for today, we'll explore what's achievable with the most popular community-run Figma MCP server, using Cursor as our MCP client.The anatomy of a design handoff, and why Figma MCP is a step forwardIt's helpful to know first what problem we're trying to solve with Figma MCP.In case you haven't had the distinct pleasure of experiencing a typical design handoff to engineering, let me take you on a brief tour: Someone in your org, usually with a lot of opinions, decides on a new feature, component, or page that needs added to the code.
Your design team creates a mockup. It is beautiful and full of potential. If you're really lucky, it's even practical to implement in code. You're often not really lucky.
You begin to think how to implement the design. Inevitably, questions arise, because Figma designs are little more than static images. What happens when you hover this button? Is there an animation on scroll? Is this still legible in tablet size?
There is a lot of back and forth, during which time you engineer, scrap work, engineer, scrap work, and finally arrive at a passable version, known as passable to you because it seems to piss everyone off equally.
Now, finally, you can do the fun part: finesse. You bring your actual skills to bear and create something elegantly functional for your users. There may be more iterations after this, but you're happy for now.Sound familiar? Hopefully, it goes better at your org.Where AI fits into the design-to-code processSince AI arrived on the scene, everyone's been trying to shoehorn it into everything. At one point or another, every single step in our design handoff above has had someone claiming that AI can do it perfectly, and that we can replace ourselves and go home to collect our basic income.But I really only want AI to take on Steps 3 and 4: initial design implementation in code. For the rest, I very much like humans in charge. This is why something like a design-to-code AI excites me. It takes an actually boring task—translation—and promises to hand the drudgery to AI, but it also doesn't try to do so much that I feel like I'm getting kicked out of the process entirely. AI scaffolds the boilerplate, and I can just edit the details.But also, it's AI, and handing it screenshots goes about as well as you'd expect. It's like if you've ever tried to draw a friend's face from memory. Sure, you can kinda tell it's them.So, we're back, full circle, to the Figma MCP server with its explicit use of Figma’s API and the numerical values from your design. Let's try it and see how much better the results may be.How to use the Figma MCP serverOkay, down to business. Feel free to follow along. We're going to:Get Figma credentials and a sample design
Get the MCP server running in CursorSet up a quick target repo
Walk through an example design to code flowStep 1: Get your Figma file and credentialsIf you've already got some Figma designs handy, great! It's more rewarding to see your own designs come to life. Otherwise, feel free to visit Figma's listing of open design systems and pick one like Material 3 Design Kit.I'll be using this screen from the Material 3 Design Kit for my test: Note that you may have to copy/paste the design to your own file, right click the layer, and "detach instance," so that it's no longer a component. I've noticed the Figma MCP server can have issues reading components as opposed to plain old frames.Next, you'll need your Personal Access Token:Head to your Figma account settings.
Go to the Security tab.
Generate a new token with the permissions and expiry date you prefer.Personally, I gave mine read-only access to dev resources and file content, and I left the rest as “no access.”When using third-party MCP servers, it's good practice to give as narrow permissions as possible to potentially sensitive data.Step 2: Set up your MCP clientNow that we've got our token, we can hop into an MCP client of your choosing.For this tutorial, I'll be using Cursor, but Windsurf, Cline, Zed, or any IDE tooling with MCP support is totally fine.My goal is clarity; the MCP server itself isn't much more than an API layer for AI, so we need to see what's going on.In Cursor, head to Cursor Settings -> MCP -> Add new global MCP server. Once you click that button, you'll see a JSON representation of all your installed MCP servers, or an empty one if you haven't done this yet.You can add the community Figma MCP server like such:{
"mcpServers": {
"Framelink Figma MCP": {
"command": "npx",
"args":}
}
}To ensure Cursor can use npx, make sure you have Node installed on your system.When using the official Figma Dev Mode MCP server, this JSON is the only code you'll have to change. Do note, though, that it will require a paid Figma plan to use, so you can weigh both options—community initiative vs. standardized support.Now, when you prompt Cursor in Agent mode, you'll see the AI make tool calls to the MCP server when you say things like, "Use the Figma MCP to..."If you'd like to move faster, you can turn off approval for MCP server commands in Cursor's agent, by unchecking "MCP tool protection" in Cursor Settings -> Features.Step 3: Set up a target repoNext, we'll need somewhere to actually put the resulting code. When using this workflow, you're not always going to be starting from scratch; good design to code means implementing Figma designs in existing repos.For our purposes today, I'll just spin up a Next.js starter template, with npx create-next-app@latest.Step 4: ShowtimeOkay, we should be all set. Select the relevant layerin Figma, copy their links, and feed it into the Cursor agent. My prompt is just:Can you replace my homepage with this Figma design? It should be a basic chat interface.
Figma frame: <;
Please use the Figma MCP server.
Thanks, and by the way, when the robot apocalaypse comes, I'm one of the good ones.Let's see it in action:And here's an example of some of the resulting code that it made:{/* Message Input */}
<div className="p-6 bg-white border-t border-">
<div className="flex items-center space-x-4">
<button className="p-2 rounded-full hover:bg-">
<svg className="w-6 h-6 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M12 2C6.48 2 2 6.48 2 12s4.48 10 10 10 10-4.48 10-10S17.52 2 12 2zm5 11h-4v4h-2v-4H7v-2h4V7h2v4h4v2z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<button className="p-2 rounded-full hover:bg-">
<svg className="w-6 h-6 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M11.99 2C6.47 2 2 6.48 2 12s4.47 10 9.99 10C17.52 22 22 17.52 22 12S17.52 2 11.99 2zM12 20c-4.42 0-8-3.58-8-8s3.58-8 8-8 8 3.58 8 8-3.58 8-8 8zm3.5-9c.83 0 1.5-.67 1.5-1.5S16.33 8 15.5 8 14 8.67 14 9.5s.67 1.5 1.5 1.5zm-7 0c.83 0 1.5-.67 1.5-1.5S9.33 8 8.5 8 7 8.67 7 9.5 7.67 11 8.5 11zm3.5 6.5c2.33 0 4.31-1.46 5.11-3.5H6.89c.8 2.04 2.78 3.5 5.11 3.5z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<div className="flex-1 relative">
<div className="flex items-center bg-rounded-full px-4 py-3">
<button className="p-1 rounded-full hover:bg-mr-3">
<svg className="w-5 h-5 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M3 18h18v-2H3v2zm0-5h18v-2H3v2zm0-7v2h18V6H3z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<input
type="text"
value={newMessage}
onChange={=> setNewMessage}
onKeyPress={handleKeyPress}
placeholder="Type a message..."
className="flex-1 bg-transparent outline-none text-placeholder-"
/>
<button
onClick={handleSendMessage}
className="p-1 rounded-full hover:bg-ml-3"
>
<svg className="w-5 h-5 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M15.5 14h-.79l-.28-.27C15.41 12.59 16 11.11 16 9.5 16 5.91 13.09 3 9.5 3S3 5.91 3 9.5 5.91 16 9.5 16c1.61 0 3.09-.59 4.23-1.57l.27.28v.79l5 4.99L20.49 19l-4.99-5zm-6 0C7.01 14 5 11.99 5 9.5S7.01 5 9.5 5 14 7.01 14 9.5 11.99 14 9.5 14z"/>
</svg>
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>In total, the AI wrote at 278-line component that mostly works, in about two minutes. Honestly, not bad for a single shot.I can use a few more prompts to clean up the code, and then go in there by hand to finesse some of the CSS, which AI never seems to get as clean as I like. But it definitely saves me time over setting this all up by hand.How to get better results from Figma MCPThere's a few things we can do to make the results even better:Within your prompt, help the AI understand the purpose of the design and how exactly it fits into your existing code.
Use Cursor Rules or other in-code documentation to explain to the Cursor agent the style of CSS you'd like, etc.
Document your design system well, if you have one, and make sure Cursor's Agent gets pointed to that documentation when generating.
Don't overwhelm the agent. Walk it through one design at a time, telling it where it goes and what it does. The process isn't fully automatic yet.Basically, it all boils down to more context, given granularly. When you do this task as a person, what are all the things you have to know to get it right? Break that down, write it in markdown files, and then point the agent there every time you need to do this task.Some markdown files you might attach in all design generations are:A design system component list
A CSS style guide
A frameworkstyle guide
Test suite rules
Explicit instructions to iterate on failed lints, TypeScript checks, and testsIndividual prompts could just include what the new component should do and how it fits in the app.Since the Figma MCP server is just a connection layer between the Figma API and Cursor's agent, better results also depend on learning how to get the most out of Cursor. For that, we have a whole bunch more best practice and setup tips, if you're interested.More than anything, don't expect perfect results. Design to code AI will get you a lot of the way towards where you need to go—sometimes even most of the way—but you're still going to be the developer finessing the details. The goal is just to save a little time. You're not trying to replace yourself.Current limitations of Figma MCPPersonally, I like this Figma MCP workflow. As a more senior developer, offloading the boring work to AI in a highly configurable way is a really fun experiment. But there's still a lot of limitations.MCP is a dev-only playground. Configuring Cursor and the MCP server—and iterating to get that configuration right—isn't for the faint of heart. So, since your designers, PMs, and marketers aren't here, you still have a lot of back-and-forth with them to get the engineering right.
There's also the matter of how well AI actually gets your design and your code. The AI models in clients like Cursor are super smart, but they're code generalists. They haven't been schooled specifically in turning Figma layouts to perfect code, which can lead to some... creative... interpretations. Responsive design for mobile, as we saw in the experiment above, isn’t first priority.
It's not a deterministic process. Even if AI has perfect access to Figma data, it can still go off the rails. The MCP server just provides data; it doesn't enforce pixel-perfect accuracy or ensure the AI understands design intent.
Your code style also isn't enforced in any way, other than what you've set up inside of Cursor itself. Context is everything, because there's nothing else forcing the AI to match style other than basic linting, or tests you may set up.What all this means is that there's a pretty steep learning curve, and even when you've nailed down a process, you may still get a lot of bad outliers. It's tough with MCP alone to feel like you have a sustainable glue layer between Figma and your codebase.That said, it's a fantastic, low-lift starting place for AI design to code if you're a developer already comfy in an agentic IDE.Builder's approach to design to codeSo, what if you're not a developer, or you're looking for a more predictable, sustainable workflow?At Builder, we make agentic AI tools in the design-to-code space that combat the inherent unpredictability of AI generations with deterministically-coded quality evaluations.Figma to code is a solved problem for us already. Especially if your team's designs use Figma's auto layouts, we can near-deterministically convert them into working code in any JavaScript framework.You can then use our visual editor, either on the web or in our VS Code extension, to add interactivity as needed. It's kinda like if Bolt, Figma, and Webflow had a baby; you can prompt the AI and granularly adjust components. Vibe code DOOM or just fix your padding. Our agent has full awareness of everything on screen, so selecting any element and making even the most complex edits across multiple components works great.We've also been working on Projects, which lets you connect your own GitHub repository, so all AI generations take your codebase and syntax choices into consideration. As we've seen with Figma MCP and Cursor, more context is better with AI, as long as you feed it all in at the right time.Projects syncs your design system across Figma and code, and you can make any change into a PRfor you and your team to review.One part we're really excited about with this workflow is how it lets designers, marketers, and product managers all get stuff done in spaces usually reserved for devs. As we've been dogfooding internally, we've seen boards of Jira papercut tickets just kinda... vanish.Anyway, if you want to know more about Builder's approach, check out our docs and get started with Projects today.So, is the Figma MCP worth your time?Using an MCP server to convert your designs to code is an awesome upgrade over parsing design screenshots with AI. Its data-rich approach gets you much farther along, much faster than developer effort alone.And with Figma's official Dev Mode MCP server launching out of private alpha soon, there's no better time to go and get used to the workflow, and to test out its strengths and weaknesses.Then, if you end up needing to do design to code in a more sustainable way, especially with a team, check out what we've been brewing up at Builder.Happy design engineering!
#design #code #with #figma #mcpDesign to Code with the Figma MCP Server
Translating your Figma designs into code can feel exactly like the kind of frustrating, low-skill gruntwork that's perfect for AI... except that most of us have also watched AI butcher hopeful screenshots into unresponsive spaghetti.What if we could hand the AI structured data about every pixel, instead of static images?This is how Figma Model Context Protocolservers work. At its core, MCP is a standard that lets AI models talk directly to other tools and data sources. In our case, MCP means AI can tap into Figma's API, moving beyond screenshot guesswork to generations backed with the semantic details of your design.Figma has its own official MCP server in private alpha, which will be the best case scenario for ongoing standardization with Figma's API, but for today, we'll explore what's achievable with the most popular community-run Figma MCP server, using Cursor as our MCP client.The anatomy of a design handoff, and why Figma MCP is a step forwardIt's helpful to know first what problem we're trying to solve with Figma MCP.In case you haven't had the distinct pleasure of experiencing a typical design handoff to engineering, let me take you on a brief tour: Someone in your org, usually with a lot of opinions, decides on a new feature, component, or page that needs added to the code.
Your design team creates a mockup. It is beautiful and full of potential. If you're really lucky, it's even practical to implement in code. You're often not really lucky.
You begin to think how to implement the design. Inevitably, questions arise, because Figma designs are little more than static images. What happens when you hover this button? Is there an animation on scroll? Is this still legible in tablet size?
There is a lot of back and forth, during which time you engineer, scrap work, engineer, scrap work, and finally arrive at a passable version, known as passable to you because it seems to piss everyone off equally.
Now, finally, you can do the fun part: finesse. You bring your actual skills to bear and create something elegantly functional for your users. There may be more iterations after this, but you're happy for now.Sound familiar? Hopefully, it goes better at your org.Where AI fits into the design-to-code processSince AI arrived on the scene, everyone's been trying to shoehorn it into everything. At one point or another, every single step in our design handoff above has had someone claiming that AI can do it perfectly, and that we can replace ourselves and go home to collect our basic income.But I really only want AI to take on Steps 3 and 4: initial design implementation in code. For the rest, I very much like humans in charge. This is why something like a design-to-code AI excites me. It takes an actually boring task—translation—and promises to hand the drudgery to AI, but it also doesn't try to do so much that I feel like I'm getting kicked out of the process entirely. AI scaffolds the boilerplate, and I can just edit the details.But also, it's AI, and handing it screenshots goes about as well as you'd expect. It's like if you've ever tried to draw a friend's face from memory. Sure, you can kinda tell it's them.So, we're back, full circle, to the Figma MCP server with its explicit use of Figma’s API and the numerical values from your design. Let's try it and see how much better the results may be.How to use the Figma MCP serverOkay, down to business. Feel free to follow along. We're going to:Get Figma credentials and a sample design
Get the MCP server running in CursorSet up a quick target repo
Walk through an example design to code flowStep 1: Get your Figma file and credentialsIf you've already got some Figma designs handy, great! It's more rewarding to see your own designs come to life. Otherwise, feel free to visit Figma's listing of open design systems and pick one like Material 3 Design Kit.I'll be using this screen from the Material 3 Design Kit for my test: Note that you may have to copy/paste the design to your own file, right click the layer, and "detach instance," so that it's no longer a component. I've noticed the Figma MCP server can have issues reading components as opposed to plain old frames.Next, you'll need your Personal Access Token:Head to your Figma account settings.
Go to the Security tab.
Generate a new token with the permissions and expiry date you prefer.Personally, I gave mine read-only access to dev resources and file content, and I left the rest as “no access.”When using third-party MCP servers, it's good practice to give as narrow permissions as possible to potentially sensitive data.Step 2: Set up your MCP clientNow that we've got our token, we can hop into an MCP client of your choosing.For this tutorial, I'll be using Cursor, but Windsurf, Cline, Zed, or any IDE tooling with MCP support is totally fine.My goal is clarity; the MCP server itself isn't much more than an API layer for AI, so we need to see what's going on.In Cursor, head to Cursor Settings -> MCP -> Add new global MCP server. Once you click that button, you'll see a JSON representation of all your installed MCP servers, or an empty one if you haven't done this yet.You can add the community Figma MCP server like such:{
"mcpServers": {
"Framelink Figma MCP": {
"command": "npx",
"args":}
}
}To ensure Cursor can use npx, make sure you have Node installed on your system.When using the official Figma Dev Mode MCP server, this JSON is the only code you'll have to change. Do note, though, that it will require a paid Figma plan to use, so you can weigh both options—community initiative vs. standardized support.Now, when you prompt Cursor in Agent mode, you'll see the AI make tool calls to the MCP server when you say things like, "Use the Figma MCP to..."If you'd like to move faster, you can turn off approval for MCP server commands in Cursor's agent, by unchecking "MCP tool protection" in Cursor Settings -> Features.Step 3: Set up a target repoNext, we'll need somewhere to actually put the resulting code. When using this workflow, you're not always going to be starting from scratch; good design to code means implementing Figma designs in existing repos.For our purposes today, I'll just spin up a Next.js starter template, with npx create-next-app@latest.Step 4: ShowtimeOkay, we should be all set. Select the relevant layerin Figma, copy their links, and feed it into the Cursor agent. My prompt is just:Can you replace my homepage with this Figma design? It should be a basic chat interface.
Figma frame: <;
Please use the Figma MCP server.
Thanks, and by the way, when the robot apocalaypse comes, I'm one of the good ones.Let's see it in action:And here's an example of some of the resulting code that it made:{/* Message Input */}
<div className="p-6 bg-white border-t border-">
<div className="flex items-center space-x-4">
<button className="p-2 rounded-full hover:bg-">
<svg className="w-6 h-6 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M12 2C6.48 2 2 6.48 2 12s4.48 10 10 10 10-4.48 10-10S17.52 2 12 2zm5 11h-4v4h-2v-4H7v-2h4V7h2v4h4v2z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<button className="p-2 rounded-full hover:bg-">
<svg className="w-6 h-6 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M11.99 2C6.47 2 2 6.48 2 12s4.47 10 9.99 10C17.52 22 22 17.52 22 12S17.52 2 11.99 2zM12 20c-4.42 0-8-3.58-8-8s3.58-8 8-8 8 3.58 8 8-3.58 8-8 8zm3.5-9c.83 0 1.5-.67 1.5-1.5S16.33 8 15.5 8 14 8.67 14 9.5s.67 1.5 1.5 1.5zm-7 0c.83 0 1.5-.67 1.5-1.5S9.33 8 8.5 8 7 8.67 7 9.5 7.67 11 8.5 11zm3.5 6.5c2.33 0 4.31-1.46 5.11-3.5H6.89c.8 2.04 2.78 3.5 5.11 3.5z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<div className="flex-1 relative">
<div className="flex items-center bg-rounded-full px-4 py-3">
<button className="p-1 rounded-full hover:bg-mr-3">
<svg className="w-5 h-5 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M3 18h18v-2H3v2zm0-5h18v-2H3v2zm0-7v2h18V6H3z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<input
type="text"
value={newMessage}
onChange={=> setNewMessage}
onKeyPress={handleKeyPress}
placeholder="Type a message..."
className="flex-1 bg-transparent outline-none text-placeholder-"
/>
<button
onClick={handleSendMessage}
className="p-1 rounded-full hover:bg-ml-3"
>
<svg className="w-5 h-5 text-" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 24 24">
<path d="M15.5 14h-.79l-.28-.27C15.41 12.59 16 11.11 16 9.5 16 5.91 13.09 3 9.5 3S3 5.91 3 9.5 5.91 16 9.5 16c1.61 0 3.09-.59 4.23-1.57l.27.28v.79l5 4.99L20.49 19l-4.99-5zm-6 0C7.01 14 5 11.99 5 9.5S7.01 5 9.5 5 14 7.01 14 9.5 11.99 14 9.5 14z"/>
</svg>
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>In total, the AI wrote at 278-line component that mostly works, in about two minutes. Honestly, not bad for a single shot.I can use a few more prompts to clean up the code, and then go in there by hand to finesse some of the CSS, which AI never seems to get as clean as I like. But it definitely saves me time over setting this all up by hand.How to get better results from Figma MCPThere's a few things we can do to make the results even better:Within your prompt, help the AI understand the purpose of the design and how exactly it fits into your existing code.
Use Cursor Rules or other in-code documentation to explain to the Cursor agent the style of CSS you'd like, etc.
Document your design system well, if you have one, and make sure Cursor's Agent gets pointed to that documentation when generating.
Don't overwhelm the agent. Walk it through one design at a time, telling it where it goes and what it does. The process isn't fully automatic yet.Basically, it all boils down to more context, given granularly. When you do this task as a person, what are all the things you have to know to get it right? Break that down, write it in markdown files, and then point the agent there every time you need to do this task.Some markdown files you might attach in all design generations are:A design system component list
A CSS style guide
A frameworkstyle guide
Test suite rules
Explicit instructions to iterate on failed lints, TypeScript checks, and testsIndividual prompts could just include what the new component should do and how it fits in the app.Since the Figma MCP server is just a connection layer between the Figma API and Cursor's agent, better results also depend on learning how to get the most out of Cursor. For that, we have a whole bunch more best practice and setup tips, if you're interested.More than anything, don't expect perfect results. Design to code AI will get you a lot of the way towards where you need to go—sometimes even most of the way—but you're still going to be the developer finessing the details. The goal is just to save a little time. You're not trying to replace yourself.Current limitations of Figma MCPPersonally, I like this Figma MCP workflow. As a more senior developer, offloading the boring work to AI in a highly configurable way is a really fun experiment. But there's still a lot of limitations.MCP is a dev-only playground. Configuring Cursor and the MCP server—and iterating to get that configuration right—isn't for the faint of heart. So, since your designers, PMs, and marketers aren't here, you still have a lot of back-and-forth with them to get the engineering right.
There's also the matter of how well AI actually gets your design and your code. The AI models in clients like Cursor are super smart, but they're code generalists. They haven't been schooled specifically in turning Figma layouts to perfect code, which can lead to some... creative... interpretations. Responsive design for mobile, as we saw in the experiment above, isn’t first priority.
It's not a deterministic process. Even if AI has perfect access to Figma data, it can still go off the rails. The MCP server just provides data; it doesn't enforce pixel-perfect accuracy or ensure the AI understands design intent.
Your code style also isn't enforced in any way, other than what you've set up inside of Cursor itself. Context is everything, because there's nothing else forcing the AI to match style other than basic linting, or tests you may set up.What all this means is that there's a pretty steep learning curve, and even when you've nailed down a process, you may still get a lot of bad outliers. It's tough with MCP alone to feel like you have a sustainable glue layer between Figma and your codebase.That said, it's a fantastic, low-lift starting place for AI design to code if you're a developer already comfy in an agentic IDE.Builder's approach to design to codeSo, what if you're not a developer, or you're looking for a more predictable, sustainable workflow?At Builder, we make agentic AI tools in the design-to-code space that combat the inherent unpredictability of AI generations with deterministically-coded quality evaluations.Figma to code is a solved problem for us already. Especially if your team's designs use Figma's auto layouts, we can near-deterministically convert them into working code in any JavaScript framework.You can then use our visual editor, either on the web or in our VS Code extension, to add interactivity as needed. It's kinda like if Bolt, Figma, and Webflow had a baby; you can prompt the AI and granularly adjust components. Vibe code DOOM or just fix your padding. Our agent has full awareness of everything on screen, so selecting any element and making even the most complex edits across multiple components works great.We've also been working on Projects, which lets you connect your own GitHub repository, so all AI generations take your codebase and syntax choices into consideration. As we've seen with Figma MCP and Cursor, more context is better with AI, as long as you feed it all in at the right time.Projects syncs your design system across Figma and code, and you can make any change into a PRfor you and your team to review.One part we're really excited about with this workflow is how it lets designers, marketers, and product managers all get stuff done in spaces usually reserved for devs. As we've been dogfooding internally, we've seen boards of Jira papercut tickets just kinda... vanish.Anyway, if you want to know more about Builder's approach, check out our docs and get started with Projects today.So, is the Figma MCP worth your time?Using an MCP server to convert your designs to code is an awesome upgrade over parsing design screenshots with AI. Its data-rich approach gets you much farther along, much faster than developer effort alone.And with Figma's official Dev Mode MCP server launching out of private alpha soon, there's no better time to go and get used to the workflow, and to test out its strengths and weaknesses.Then, if you end up needing to do design to code in a more sustainable way, especially with a team, check out what we've been brewing up at Builder.Happy design engineering!
#design #code #with #figma #mcp