Managers rethink ecological scenarios as threats rise amid climate change
In Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks in California, trees that have persisted through rain and shine for thousands of years are now facing multiple threats triggered by a changing climate.
Scientists and park managers once thought giant sequoia forests were nearly impervious to stressors like wildfire, drought and pests. Yet, even very large trees are proving vulnerable, particularly when those stressors are amplified by rising temperatures and increasing weather extremes.
The rapid pace of climate change—combined with threats like the spread of invasive species and diseases—can affect ecosystems in ways that defy expectations based on past experiences. As a result, Western forests are transitioning to grasslands or shrublands after unprecedented wildfires. Woody plants are expanding into coastal wetlands. Coral reefs are being lost entirely.
To protect these places, which are valued for their natural beauty and the benefits they provide for recreation, clean water and wildlife, forest and land managers increasingly must anticipate risks they have never seen before. And they must prepare for what those risks will mean for stewardship as ecosystems rapidly transform.
As ecologists and a climate scientist, we’re helping them figure out how to do that.
Managing changing ecosystems
Traditional management approaches focus on maintaining or restoring how ecosystems looked and functioned historically.
However, that doesn’t always work when ecosystems are subjected to new and rapidly shifting conditions.
Ecosystems have many moving parts—plants, animals, fungi, and microbes; and the soil, air and water in which they live—that interact with one another in complex ways.
When the climate changes, it’s like shifting the ground on which everything rests. The results can undermine the integrity of the system, leading to ecological changes that are hard to predict.
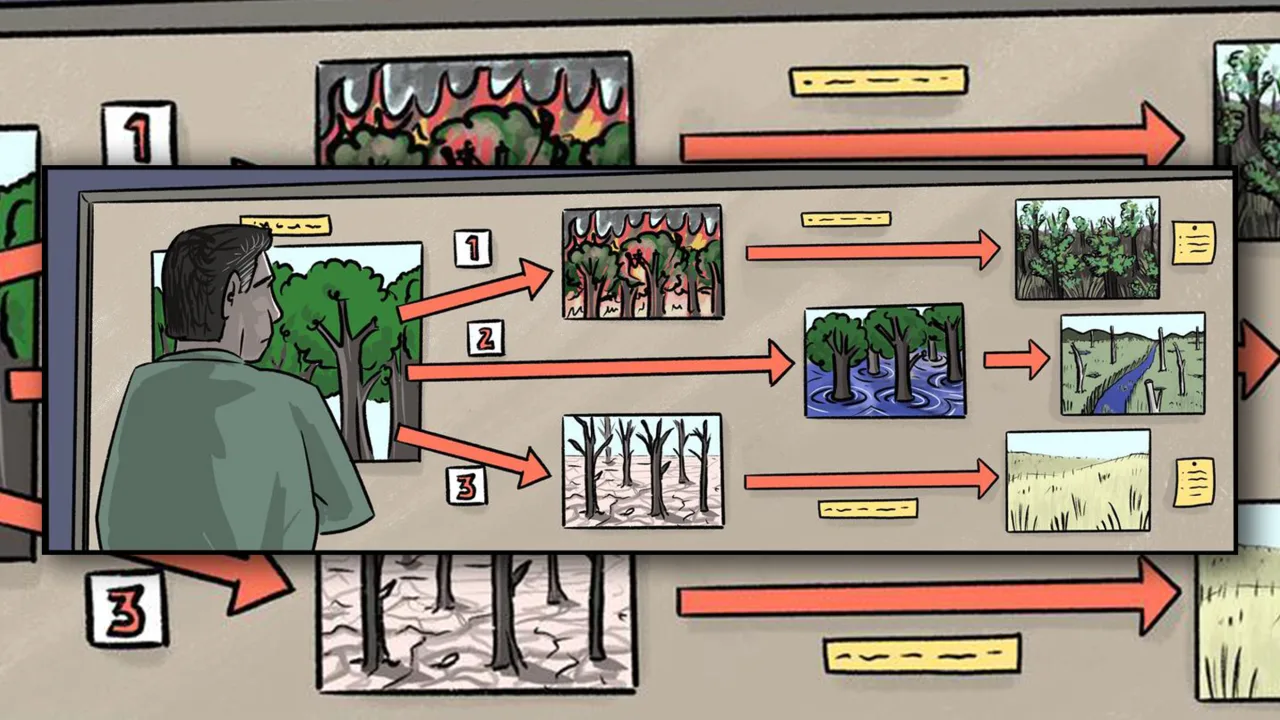
To plan for an uncertain future, natural resource managers need to consider many different ways changes in climate and ecosystems could affect their landscapes. Essentially, what scenarios are possible?
Preparing for multiple possibilities
At Sequoia and Kings Canyon, park managers were aware that climate change posed some big risks to the iconic trees under their care. More than a decade ago, they undertook a major effort to explore different scenarios that could play out in the future.
It’s a good thing they did, because some of the more extreme possibilities they imagined happened sooner than expected.
In 2014, drought in California caused the giant sequoias’ foliage to die back, something never documented before. In 2017, sequoia trees began dying from insect damage. And, in 2020 and 2021, fires burned through sequoia groves, killing thousands of ancient trees.
While these extreme events came as a surprise to many people, thinking through the possibilities ahead of time meant the park managers had already begun to take steps that proved beneficial. One example was prioritizing prescribed burns to remove undergrowth that could fuel hotter, more destructive fires.
The key to effective planning is a thoughtful consideration of a suite of strategies that are likely to succeed in the face of many different changes in climates and ecosystems. That involves thinking through wide-ranging potential outcomes to see how different strategies might fare under each scenario—including preparing for catastrophic possibilities, even those considered unlikely.
For example, prescribed burning may reduce risks from both catastrophic wildfire and drought by reducing the density of plant growth, whereas suppressing all fires could increase those risks in the long run.
Strategies undertaken today have consequences for decades to come. Managers need to have confidence that they are making good investments when they put limited resources toward actions like forest thinning, invasive species control, buying seeds or replanting trees. Scenarios can help inform those investment choices.
Constructing credible scenarios of ecological change to inform this type of planning requires considering the most important unknowns. Scenarios look not only at how the climate could change, but also how complex ecosystems could react and what surprises might lay beyond the horizon.
Scientists at the North Central Climate Adaptation Science Center are collaborating with managers in the Nebraska Sandhills to develop scenarios of future ecological change under different climate conditions, disturbance events like fires and extreme droughts, and land uses like grazing. Key ingredients for crafting ecological scenarios
To provide some guidance to people tasked with managing these landscapes, we brought together a group of experts in ecology, climate science, and natural resource management from across universities and government agencies.
We identified three key ingredients for constructing credible ecological scenarios:
1. Embracing ecological uncertainty: Instead of banking on one “most likely” outcome for ecosystems in a changing climate, managers can better prepare by mapping out multiple possibilities. In Nebraska’s Sandhills, we are exploring how this mostly intact native prairie could transform, with outcomes as divergent as woodlands and open dunes.
2. Thinking in trajectories: It’s helpful to consider not just the outcomes, but also the potential pathways for getting there. Will ecological changes unfold gradually or all at once? By envisioning different pathways through which ecosystems might respond to climate change and other stressors, natural resource managers can identify critical moments where specific actions, such as removing tree seedlings encroaching into grasslands, can steer ecosystems toward a more desirable future.
3. Preparing for surprises: Planning for rare disasters or sudden species collapses helps managers respond nimbly when the unexpected strikes, such as a severe drought leading to widespread erosion. Being prepared for abrupt changes and having contingency plans can mean the difference between quickly helping an ecosystem recover and losing it entirely.
Over the past decade, access to climate model projections through easy-to-use websites has revolutionized resource managers’ ability to explore different scenarios of how the local climate might change.
What managers are missing today is similar access to ecological model projections and tools that can help them anticipate possible changes in ecosystems. To bridge this gap, we believe the scientific community should prioritize developing ecological projections and decision-support tools that can empower managers to plan for ecological uncertainty with greater confidence and foresight.
Ecological scenarios don’t eliminate uncertainty, but they can help to navigate it more effectively by identifying strategic actions to manage forests and other ecosystems.
Kyra Clark-Wolf is a research scientist in ecological transformation at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Brian W. Miller is a research ecologist at the U.S. Geological Survey.
Imtiaz Rangwala is a research scientist in climate at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
#managers #rethink #ecological #scenarios #threats
Managers rethink ecological scenarios as threats rise amid climate change
In Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks in California, trees that have persisted through rain and shine for thousands of years are now facing multiple threats triggered by a changing climate.
Scientists and park managers once thought giant sequoia forests were nearly impervious to stressors like wildfire, drought and pests. Yet, even very large trees are proving vulnerable, particularly when those stressors are amplified by rising temperatures and increasing weather extremes.
The rapid pace of climate change—combined with threats like the spread of invasive species and diseases—can affect ecosystems in ways that defy expectations based on past experiences. As a result, Western forests are transitioning to grasslands or shrublands after unprecedented wildfires. Woody plants are expanding into coastal wetlands. Coral reefs are being lost entirely.
To protect these places, which are valued for their natural beauty and the benefits they provide for recreation, clean water and wildlife, forest and land managers increasingly must anticipate risks they have never seen before. And they must prepare for what those risks will mean for stewardship as ecosystems rapidly transform.
As ecologists and a climate scientist, we’re helping them figure out how to do that.
Managing changing ecosystems
Traditional management approaches focus on maintaining or restoring how ecosystems looked and functioned historically.
However, that doesn’t always work when ecosystems are subjected to new and rapidly shifting conditions.
Ecosystems have many moving parts—plants, animals, fungi, and microbes; and the soil, air and water in which they live—that interact with one another in complex ways.
When the climate changes, it’s like shifting the ground on which everything rests. The results can undermine the integrity of the system, leading to ecological changes that are hard to predict.
To plan for an uncertain future, natural resource managers need to consider many different ways changes in climate and ecosystems could affect their landscapes. Essentially, what scenarios are possible?
Preparing for multiple possibilities
At Sequoia and Kings Canyon, park managers were aware that climate change posed some big risks to the iconic trees under their care. More than a decade ago, they undertook a major effort to explore different scenarios that could play out in the future.
It’s a good thing they did, because some of the more extreme possibilities they imagined happened sooner than expected.
In 2014, drought in California caused the giant sequoias’ foliage to die back, something never documented before. In 2017, sequoia trees began dying from insect damage. And, in 2020 and 2021, fires burned through sequoia groves, killing thousands of ancient trees.
While these extreme events came as a surprise to many people, thinking through the possibilities ahead of time meant the park managers had already begun to take steps that proved beneficial. One example was prioritizing prescribed burns to remove undergrowth that could fuel hotter, more destructive fires.
The key to effective planning is a thoughtful consideration of a suite of strategies that are likely to succeed in the face of many different changes in climates and ecosystems. That involves thinking through wide-ranging potential outcomes to see how different strategies might fare under each scenario—including preparing for catastrophic possibilities, even those considered unlikely.
For example, prescribed burning may reduce risks from both catastrophic wildfire and drought by reducing the density of plant growth, whereas suppressing all fires could increase those risks in the long run.
Strategies undertaken today have consequences for decades to come. Managers need to have confidence that they are making good investments when they put limited resources toward actions like forest thinning, invasive species control, buying seeds or replanting trees. Scenarios can help inform those investment choices.
Constructing credible scenarios of ecological change to inform this type of planning requires considering the most important unknowns. Scenarios look not only at how the climate could change, but also how complex ecosystems could react and what surprises might lay beyond the horizon.
Scientists at the North Central Climate Adaptation Science Center are collaborating with managers in the Nebraska Sandhills to develop scenarios of future ecological change under different climate conditions, disturbance events like fires and extreme droughts, and land uses like grazing. Key ingredients for crafting ecological scenarios
To provide some guidance to people tasked with managing these landscapes, we brought together a group of experts in ecology, climate science, and natural resource management from across universities and government agencies.
We identified three key ingredients for constructing credible ecological scenarios:
1. Embracing ecological uncertainty: Instead of banking on one “most likely” outcome for ecosystems in a changing climate, managers can better prepare by mapping out multiple possibilities. In Nebraska’s Sandhills, we are exploring how this mostly intact native prairie could transform, with outcomes as divergent as woodlands and open dunes.
2. Thinking in trajectories: It’s helpful to consider not just the outcomes, but also the potential pathways for getting there. Will ecological changes unfold gradually or all at once? By envisioning different pathways through which ecosystems might respond to climate change and other stressors, natural resource managers can identify critical moments where specific actions, such as removing tree seedlings encroaching into grasslands, can steer ecosystems toward a more desirable future.
3. Preparing for surprises: Planning for rare disasters or sudden species collapses helps managers respond nimbly when the unexpected strikes, such as a severe drought leading to widespread erosion. Being prepared for abrupt changes and having contingency plans can mean the difference between quickly helping an ecosystem recover and losing it entirely.
Over the past decade, access to climate model projections through easy-to-use websites has revolutionized resource managers’ ability to explore different scenarios of how the local climate might change.
What managers are missing today is similar access to ecological model projections and tools that can help them anticipate possible changes in ecosystems. To bridge this gap, we believe the scientific community should prioritize developing ecological projections and decision-support tools that can empower managers to plan for ecological uncertainty with greater confidence and foresight.
Ecological scenarios don’t eliminate uncertainty, but they can help to navigate it more effectively by identifying strategic actions to manage forests and other ecosystems.
Kyra Clark-Wolf is a research scientist in ecological transformation at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Brian W. Miller is a research ecologist at the U.S. Geological Survey.
Imtiaz Rangwala is a research scientist in climate at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
#managers #rethink #ecological #scenarios #threats
0 Reacties
·0 aandelen
·0 voorbeeld